Coursera: Machine Learning (Week 3) Quiz - Logistic Regression | Andrew NG
Recommended Courses:
1.Logistic Regression
Don't just copy & paste for the sake of completion. The solutions uploaded here are only for reference.They are meant to unblock you if you get stuck somewhere.Make sure you understand first.
- Suppose that you have trained a logistic regression classifier, and it outputs on a new example a prediction
= 0.2. This means (check all that apply):
- Our estimate for P(y = 1|x; θ) is 0.8.
- Our estimate for P(y = 0|x; θ) is 0.8.
- Our estimate for P(y = 1|x; θ) is 0.2.
- Our estimate for P(y = 0|x; θ) is 0.2.
- Suppose you have the following training set, and fit a logistic regression classifier
.

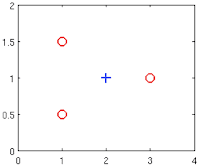
Which of the following are true? Check all that apply.- Adding polynomial features (e.g., instead using
- At the optimal value of θ (e.g., found by fminunc), we will have J(θ) ≥ 0.
- Adding polynomial features (e.g., instead using
) would increase J(θ) because we are now summing over more terms.
- If we train gradient descent for enough iterations, for some examples
in the training set it is possible to obtain
.
- For logistic regression, the gradient is given by
. Which of these is a correct gradient descent update for logistic regression with a learning rate of
? Check all that apply.
- Which of the following statements are true? Check all that apply.
- The one-vs-all technique allows you to use logistic regression for problems in which each
comes from a fixed, discrete set of values.
- For logistic regression, sometimes gradient descent will converge to a local minimum (and fail to find the global minimum). This is the reason we prefer more advanced optimization algorithms such as fminunc (conjugate gradient/BFGS/L-BFGS/etc).
- The cost function
for logistic regression trained with
examples is always greater than or equal to zero.
- Since we train one classifier when there are two classes, we train two classifiers when there are three classes (and we do one-vs-all classification).
- 5.Suppose you train a logistic classifier
. Suppose
,
,
. Which of the following figures represents the decision boundary found by your classifier?
- Figure:
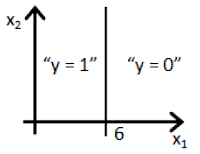 ANSWER
ANSWER - Figure:
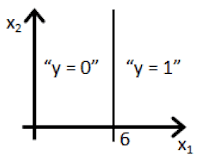
- Figure:

- Figure:
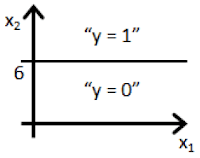
- 一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一一
- Machine Learning Coursera-All weeks solutions [Assignment + Quiz] click here&Have no concerns to ask doubts in the comment section. I will give my best to answer it.If you find this helpful kindly comment and share the post.This is the simplest way to encourage me to keep doing such work.Thanks & Regards,- Wolf
- Figure:
- The one-vs-all technique allows you to use logistic regression for problems in which each


Comments
Post a Comment